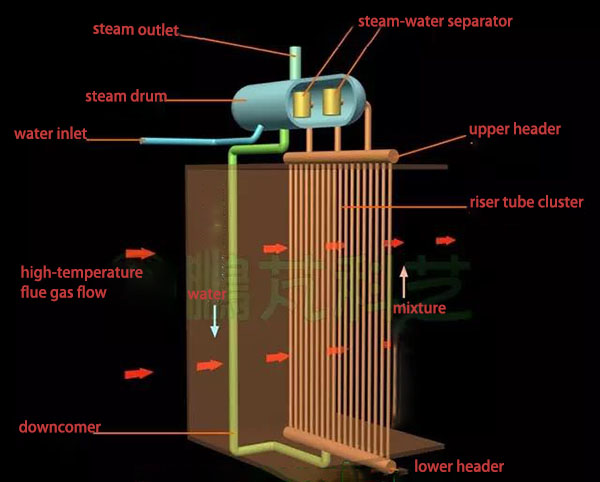
Steam boiler principle is very easy to understand, and the model diagram below includes riser, steam drum and downcomer. The riser is a cluster of dense pipes, which is connected by upper and lower header. The upper header connects to steam drum through steam introduction pipe, and steam drum connects to lower header through downcomer. The riser tube cluster, steam drum and downcomer form a loop. The riser tube clusters are in the furnace, and steam drum and downcomer are outside the furnace.
When water enters the steam drum, water fills the riser tube cluster and downcomer. The water level shall be near the centerline of the steam drum. When the high-temperature flue gas passes through the outside of tube cluster, the water is heated into a steam-water mixture. The water in the downcomer absorbs no heat at all. The density of steam-water mixture in the tube cluster is smaller than that in the downcomer. A pressure difference forms in lower header, which pushes the steam-water mixture in riser into steam drum. The water in the downcomer enters the riser, forming natural circulation.
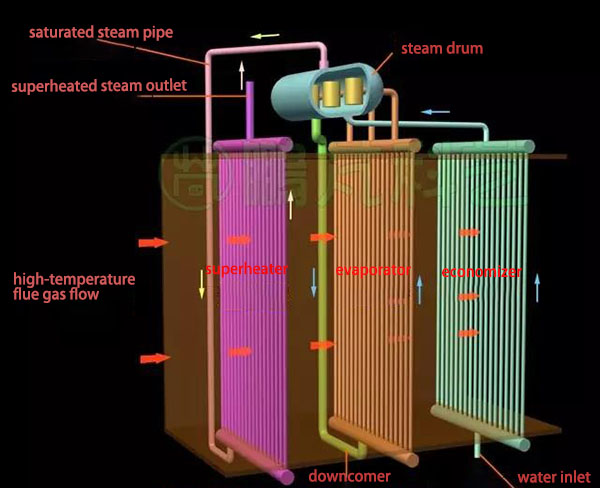
Steam drum is an important hub for water heating, evaporation and overheating to ensure normal water circulation. After entering the steam drum, the steam-water mixture is separated into saturated steam and water by a steam-water separator. The saturated steam outputs through the steam outlet above the steam drum; the separated water enters the downcomer. The riser tube cluster to generate saturated steam has a name of evaporator. Power plant boiler also has economizer and superheater, which also comprises tube cluster. The water is first heated in the economizer, and then enters the evaporator through steam drum and downcomer. This process improves the efficiency of both evaporator and steam boiler. The saturated steam generated by evaporator outputs through steam drum, and then enters the superheater to become superheated steam.
Post time: Sep-26-2021